Transhumanism In Film on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement which advocates the enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available sophisticated technologies that can greatly enhance longevity and cognition.
Transhumanist thinkers study the potential benefits and dangers of emerging technologies that could overcome fundamental human limitations as well as the
 Fundamental ideas of transhumanism were first advanced in 1923 by the British geneticist
Fundamental ideas of transhumanism were first advanced in 1923 by the British geneticist
 While many transhumanist theorists and advocates seek to apply
While many transhumanist theorists and advocates seek to apply
 As proponents of self-improvement and body modification, transhumanists tend to use existing technologies and techniques that supposedly improve cognitive and physical performance, while engaging in routines and lifestyles designed to improve health and longevity. Depending on their age, some transhumanists express concern that they will not live to reap the benefits of future technologies. However, many have a great interest in life extension strategies and in funding research in
As proponents of self-improvement and body modification, transhumanists tend to use existing technologies and techniques that supposedly improve cognitive and physical performance, while engaging in routines and lifestyles designed to improve health and longevity. Depending on their age, some transhumanists express concern that they will not live to reap the benefits of future technologies. However, many have a great interest in life extension strategies and in funding research in
 In his 2003 book ''Enough: Staying Human in an Engineered Age'', environmental ethics, environmental ethicist Bill McKibben argued at length against many of the technologies that are postulated or supported by transhumanists, including germinal choice technology, nanomedicine and life extension strategies. He claims that it would be morally wrong for humans to tamper with fundamental aspects of themselves (or their children) in an attempt to overcome universal human limitations, such as vulnerability to aging, maximum life span and biological constraints on physical and cognitive ability. Attempts to "improve" themselves through such manipulation would remove limitations that provide a necessary context for the experience of meaningful human choice. He claims that human lives would no longer seem Meaning of life, meaningful in a world where such limitations could be overcome technologically. Even the goal of using germinal choice technology for clearly therapeutic purposes should be relinquished, since it would inevitably produce temptations to tamper with such things as cognitive capacities. He argues that it is possible for societies to benefit from renouncing particular technologies, using as examples Ming Dynasty, Ming China, Tokugawa shogunate, Tokugawa Japan and the contemporary Amish.
Biopolitical activist Jeremy Rifkin and biologist Stuart Newman accept that biotechnology has the power to make profound changes in organismal identity. They argue against the genetic engineering of human beings because they fear the blurring of the boundary between human and Cultural artifact, artifact. Philosopher Keekok Lee sees such developments as part of an accelerating trend in modernization in which technology has been used to transform the "natural" into the "artefactual". In the extreme, this could lead to the manufacturing and enslavement of "monsters" such as human clones, human-animal hybrid, human-animal chimera (genetics), chimeras, or bioroids, but even lesser dislocations of humans and non-humans from social structure, social and ecosystem, ecological systems are seen as problematic. The film ''Blade Runner'' (1982) and the novels ''The Boys from Brazil (novel), The Boys From Brazil'' (1976) and ''The Island of Doctor Moreau'' (1896) depict elements of such scenarios, but Mary Shelley's 1818 novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus '' is most often alluded to by critics who suggest that biotechnologies could create objectification, objectified and anomie, socially unmoored people as well as untermensch, subhumans. Such critics propose that strict measures be implemented to prevent what they portray as dehumanization, dehumanizing possibilities from ever happening, usually in the form of an international ban (law), ban on human genetic engineering.
Science journalist Ronald Bailey claims that McKibben's historical examples are flawed and support different conclusions when studied more closely. For example, few groups are more cautious than the Amish about embracing new technologies, but, though they shun television and use horses and buggies, some are welcoming the possibilities of gene therapy since inbreeding has afflicted them with a number of rare genetic diseases. Bailey and other supporters of technological alteration of human biology also reject the claim that life would be experienced as meaningless if some human limitations are overcome with enhancement technologies as extremely subjective.
Writing in ''Reason (magazine), Reason'' magazine, Bailey has accused opponents of research involving the modification of animals as indulging in alarmism when they speculate about the creation of subhuman creatures with human-like intelligence and brains resembling those of ''Homo sapiens''. Bailey insists that the aim of conducting research on animals is simply to produce human health care benefits.
A different response comes from transhumanist personhood theory, personhood theorists who object to what they characterize as the anthropomorphobia fueling some criticisms of this research, which science fiction writer Isaac Asimov termed the "Frankenstein complex". For example, Woody Evans argues that, provided they are self-aware, human clones, human-animal chimeras and biological uplift, uplifted animals would all be unique persons deserving of respect, dignity, rights, responsibilities, and citizenship. They conclude that the coming ethical issue is not the creation of so-called monsters, but what they characterize as the "wisdom of repugnance, yuck factor" and "Human exceptionalism, human-racism", that would judge and treat these creations as monstrous. In book 3 of his ''Corrupting the Image'' series, Dr. Douglas Hamp goes so far as to suggest that the Beast of John's Apocalypse is himself a hybrid who will induce humanity to take "the Number of the beast, mark of the Beast," in the hopes of obtaining perfection and immortality.
At least one public interest organization, the U.S.-based Center for Genetics and Society, was formed, in 2001, with the specific goal of opposing transhumanist agendas that involve transgenerational modification of human biology, such as full-term human cloning and germinal choice technology. The Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future of the Chicago-Kent College of Law critically scrutinizes proposed applications of genetic and nanotechnologies to human biology in an academic setting.
In his 2003 book ''Enough: Staying Human in an Engineered Age'', environmental ethics, environmental ethicist Bill McKibben argued at length against many of the technologies that are postulated or supported by transhumanists, including germinal choice technology, nanomedicine and life extension strategies. He claims that it would be morally wrong for humans to tamper with fundamental aspects of themselves (or their children) in an attempt to overcome universal human limitations, such as vulnerability to aging, maximum life span and biological constraints on physical and cognitive ability. Attempts to "improve" themselves through such manipulation would remove limitations that provide a necessary context for the experience of meaningful human choice. He claims that human lives would no longer seem Meaning of life, meaningful in a world where such limitations could be overcome technologically. Even the goal of using germinal choice technology for clearly therapeutic purposes should be relinquished, since it would inevitably produce temptations to tamper with such things as cognitive capacities. He argues that it is possible for societies to benefit from renouncing particular technologies, using as examples Ming Dynasty, Ming China, Tokugawa shogunate, Tokugawa Japan and the contemporary Amish.
Biopolitical activist Jeremy Rifkin and biologist Stuart Newman accept that biotechnology has the power to make profound changes in organismal identity. They argue against the genetic engineering of human beings because they fear the blurring of the boundary between human and Cultural artifact, artifact. Philosopher Keekok Lee sees such developments as part of an accelerating trend in modernization in which technology has been used to transform the "natural" into the "artefactual". In the extreme, this could lead to the manufacturing and enslavement of "monsters" such as human clones, human-animal hybrid, human-animal chimera (genetics), chimeras, or bioroids, but even lesser dislocations of humans and non-humans from social structure, social and ecosystem, ecological systems are seen as problematic. The film ''Blade Runner'' (1982) and the novels ''The Boys from Brazil (novel), The Boys From Brazil'' (1976) and ''The Island of Doctor Moreau'' (1896) depict elements of such scenarios, but Mary Shelley's 1818 novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus '' is most often alluded to by critics who suggest that biotechnologies could create objectification, objectified and anomie, socially unmoored people as well as untermensch, subhumans. Such critics propose that strict measures be implemented to prevent what they portray as dehumanization, dehumanizing possibilities from ever happening, usually in the form of an international ban (law), ban on human genetic engineering.
Science journalist Ronald Bailey claims that McKibben's historical examples are flawed and support different conclusions when studied more closely. For example, few groups are more cautious than the Amish about embracing new technologies, but, though they shun television and use horses and buggies, some are welcoming the possibilities of gene therapy since inbreeding has afflicted them with a number of rare genetic diseases. Bailey and other supporters of technological alteration of human biology also reject the claim that life would be experienced as meaningless if some human limitations are overcome with enhancement technologies as extremely subjective.
Writing in ''Reason (magazine), Reason'' magazine, Bailey has accused opponents of research involving the modification of animals as indulging in alarmism when they speculate about the creation of subhuman creatures with human-like intelligence and brains resembling those of ''Homo sapiens''. Bailey insists that the aim of conducting research on animals is simply to produce human health care benefits.
A different response comes from transhumanist personhood theory, personhood theorists who object to what they characterize as the anthropomorphobia fueling some criticisms of this research, which science fiction writer Isaac Asimov termed the "Frankenstein complex". For example, Woody Evans argues that, provided they are self-aware, human clones, human-animal chimeras and biological uplift, uplifted animals would all be unique persons deserving of respect, dignity, rights, responsibilities, and citizenship. They conclude that the coming ethical issue is not the creation of so-called monsters, but what they characterize as the "wisdom of repugnance, yuck factor" and "Human exceptionalism, human-racism", that would judge and treat these creations as monstrous. In book 3 of his ''Corrupting the Image'' series, Dr. Douglas Hamp goes so far as to suggest that the Beast of John's Apocalypse is himself a hybrid who will induce humanity to take "the Number of the beast, mark of the Beast," in the hopes of obtaining perfection and immortality.
At least one public interest organization, the U.S.-based Center for Genetics and Society, was formed, in 2001, with the specific goal of opposing transhumanist agendas that involve transgenerational modification of human biology, such as full-term human cloning and germinal choice technology. The Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future of the Chicago-Kent College of Law critically scrutinizes proposed applications of genetic and nanotechnologies to human biology in an academic setting.
H+Pedia
Transhumanist Wiki
What is Transhumanism?
*Future of Humanity Institute *Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future {{Authority control Transhumanism, 1990 introductions Bioethics Body modification Doomsday scenarios, * Emerging technologies Ethics of science and technology Existential risk from artificial general intelligence Ideologies Immortality Metaphysics Ontology Philosophical movements Philosophy of artificial intelligence Philosophy of culture Philosophy of science Philosophy of technology Philosophical anthropology Posthumanism Science fiction culture Science fiction themes Singularitarianism Singularity theory Social change Social philosophy Subcultures Technological change Technology development Technology forecasting Technology hazards Theory of mind Transhumanist politics Technological utopianism
ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concer ...
of using such technologies. Some transhumanists believe that human beings may eventually be able to transform themselves into beings with abilities so greatly expanded from the current condition as to merit the label of posthuman beings.
Another topic of transhumanist research is how to protect humanity against existential risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
s, such as nuclear war or asteroid collision.
Julian Huxley was a biologist who popularised the term transhumanism in an influential 1957 essay. The contemporary meaning of the term "transhumanism" was foreshadowed by one of the first professors of futurology
Futures studies, futures research, futurism or futurology is the systematic, interdisciplinary and holistic study of social and technological advancement, and other environmental trends, often for the purpose of exploring how people will li ...
, a man who changed his name to FM-2030. In the 1960s, he taught "new concepts of the human" at The New School
The New School is a private research university in New York City. It was founded in 1919 as The New School for Social Research with an original mission dedicated to academic freedom and intellectual inquiry and a home for progressive thinkers. ...
when he began to identify people who adopt technologies, lifestyles, and worldview
A worldview or world-view or ''Weltanschauung'' is the fundamental cognitive orientation of an individual or society encompassing the whole of the individual's or society's knowledge, culture, and point of view. A worldview can include natural ...
s "transitional" to posthumanity as "transhuman
Transhuman, or trans-human, is the concept of an intermediary form between human and posthuman. In other words, a transhuman is a being that resembles a human in most respects but who has powers and abilities beyond those of standard humans. Th ...
". The assertion would lay the intellectual groundwork for the British philosopher Max More to begin articulating the principles of transhumanism as a futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities abo ...
philosophy in 1990, and organizing in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
a school of thought
A school of thought, or intellectual tradition, is the perspective of a group of people who share common characteristics of opinion or outlook of a philosophy, discipline, belief, social movement, economics, cultural movement, or art movement.
...
that has since grown into the worldwide transhumanist movement.
Influenced by seminal works of science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
, the transhumanist vision of a transformed future humanity has attracted many supporters and detractors from a wide range of perspectives, including philosophy and religion.
In 2017, Penn State University Press
The Penn State University Press, also known as The Pennsylvania State University Press, was established in 1956 and is a non-profit publisher of scholarly books and journals. It is the independent publishing branch of the Pennsylvania State Un ...
, in cooperation with philosopher Stefan Lorenz Sorgner and sociologist James Hughes, established the '' Journal of Posthuman Studies'' as the first academic journal explicitly dedicated to the posthuman, with the goal of clarifying the notions of posthumanism
Posthumanism or post-humanism (meaning "after humanism" or "beyond humanism") is an idea in continental philosophy and critical theory responding to the presence of anthropocentrism in 21st century thought. It encompasses a wide variety of b ...
and transhumanism, as well as comparing and contrasting both.
History
Precursors of transhumanism
According to Nick Bostrom, transcendentalist impulses have been expressed at least as far back as the quest forimmortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality.
Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immorta ...
in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with ...
'', as well as in historical quests for the Fountain of Youth
The Fountain of Youth is a mythical spring which allegedly restores the youth of anyone who drinks or bathes in its waters. Tales of such a fountain have been recounted around the world for thousands of years, appearing in the writings of Herod ...
, the Elixir of Life
The elixir of life, also known as elixir of immortality, is a potion that supposedly grants the drinker eternal life and/or eternal youth. This elixir was also said to cure all diseases. Alchemists in various ages and cultures sought the means ...
, and other efforts to stave off aging and death.
In his Divine Comedy
The ''Divine Comedy'' ( it, Divina Commedia ) is an Italian narrative poem by Dante Alighieri, begun 1308 and completed in around 1321, shortly before the author's death. It is widely considered the pre-eminent work in Italian literature ...
, Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian people, Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', origin ...
coined the word ''trasumanar'' meaning "to transcend human nature, to pass beyond human nature" in the first canto
The canto () is a principal form of division in medieval and modern long poetry.
Etymology and equivalent terms
The word ''canto'' is derived from the Italian word for "song" or "singing", which comes from the Latin ''cantus'', "song", from the ...
of Paradiso.
One of the early precursors to transhumanist ideas is Discourse on Method
''Discourse on the Method of Rightly Conducting One's Reason and of Seeking Truth in the Sciences'' (french: Discours de la Méthode Pour bien conduire sa raison, et chercher la vérité dans les sciences) is a philosophical and autobiographical ...
(1637) by René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Ma ...
. In the Discourse, Descartes envisioned a new kind of medicine that could grant both physical immortality and stronger minds.
In his first edition of ''Political Justice
''Enquiry Concerning Political Justice and its Influence on Morals and Happiness'' is a 1793 book by the philosopher William Godwin, in which the author outlines his political philosophy. It is the first modern work to expound anarchism.
Backg ...
'' (1793), William Godwin included arguments favoring the possibility of "earthly immortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality.
Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immorta ...
" (what would now be called physical immortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality.
Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immorta ...
). Godwin explored the themes of life extension and immortality in his gothic novel ''St. Leon'', which became popular (and notorious) at the time of its publication in 1799, but is now mostly forgotten. ''St. Leon'' may have provided inspiration for his daughter Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel '' Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an early example of science fiction. She also ...
's novel ''Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a sapient creature in an unorthodox scientific ...
''.
There is debate about whether the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Nietzsche (1844–1900) developed his philosophy during the late 19th century. He owed the awakening of his philosophical interest to reading Arthur Schopenhauer's ''Die Welt als Wille und Vorstellung'' (''The World as Will and Represe ...
can be considered an influence on transhumanism, despite its exaltation of the "Übermensch
The (; "Overhuman") is a concept in the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche. In his 1883 book ''Thus Spoke Zarathustra'' (german: Also sprach Zarathustra), Nietzsche has his character Zarathustra posit the as a goal for humanity to set for itse ...
" (overman or superman), due to its emphasis on self-actualization
Self-actualization, in Maslow's hierarchy of needs, is the highest level of psychological development, where personal potential is fully realized after basic bodily and ego needs have been fulfilled.
Self-actualization was coined by the organis ...
rather than technological transformation. The transhumanist philosophies of Max More and Stefan Lorenz Sorgner have been influenced strongly by Nietzschean thinking. By way of contrast, The Transhumanist Declaration ''"...advocates the well-being of all sentience (whether in artificial intellects, humans, posthumans, or non-human animals)".
The late 19th to early 20th century movement known as Russian cosmism
Russian cosmism, also cosmism, is a philosophical and cultural movement that emerged in Russia at the turn of the 19th century, and again, at the beginning of the 20th century. At the beginning of the 20th century, there was a burst of scientifi ...
, by Russian philosopher N. F. Fyodorov, is noted for anticipating transhumanist ideas.
Early transhumanist thinking
 Fundamental ideas of transhumanism were first advanced in 1923 by the British geneticist
Fundamental ideas of transhumanism were first advanced in 1923 by the British geneticist J. B. S. Haldane
John Burdon Sanderson Haldane (; 5 November 18921 December 1964), nicknamed "Jack" or "JBS", was a British-Indian scientist who worked in physiology, genetics, evolutionary biology, and mathematics. With innovative use of statistics in biolog ...
in his essay '' Daedalus: Science and the Future'', which predicted that great benefits would come from the application of advanced sciences to human biology—and that every such advance would first appear to someone as blasphemy or perversion, "indecent and unnatural". In particular, he was interested in the development of the science of eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior o ...
, ectogenesis
Ectogenesis (from the Greek ''ἐκτός'', "outside," and ''genesis'') is the growth of an organism in an artificial environment outside the body in which it would normally be found, such as the growth of an embryo or fetus outside the mother's ...
(creating and sustaining life in an artificial environment), and the application of genetics to improve human characteristics, such as health and intelligence.
His article inspired academic and popular interest. J. D. Bernal, a crystallographer at Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
, wrote ''The World, the Flesh and the Devil'' in 1929, in which he speculated on the prospects of space colonization
Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory.
The inhabitation and territor ...
and radical changes to human bodies and intelligence through bionic implants and cognitive enhancement
Neuroenhancement or cognitive enhancement refers to the targeted enhancement and extension of cognitive and affective abilities based on an understanding of their underlying neurobiology in healthy persons who do not have any mental illness. As su ...
. These ideas have been common transhumanist themes ever since.
The biologist Julian Huxley is generally regarded as the founder of transhumanism after using the term for the title of an influential 1957 article. The term itself, however, derives from an earlier 1940 paper by the Canadian philosopher W. D. Lighthall. Huxley describes transhumanism in these terms:
Huxley's definition differs, albeit not substantially, from the one commonly in use since the 1980s. The ideas raised by these thinkers were explored in the science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
of the 1960s, notably in Arthur C. Clarke's '' 2001: A Space Odyssey'', in which an alien artifact grants transcendent power to its wielder.
Japanese Metabolist
was a post-war Japanese architectural movement that fused ideas about architectural megastructures with those of organic biological growth. It had its first international exposure during CIAM's 1959 meeting and its ideas were tentatively teste ...
architects produced a manifesto in 1960 which outlined goals to "encourage active metabolic development of our society" through design and technology. In the Material and Man section of the manifesto, Noboru Kawazoe suggests that:After several decades, with the rapid progress of communication technology, every one will have a "brain wave receiver" in his ear, which conveys directly and exactly what other people think about him and vice versa. What I think will be known by all the people. There is no more individual consciousness, only the will of mankind as a whole.
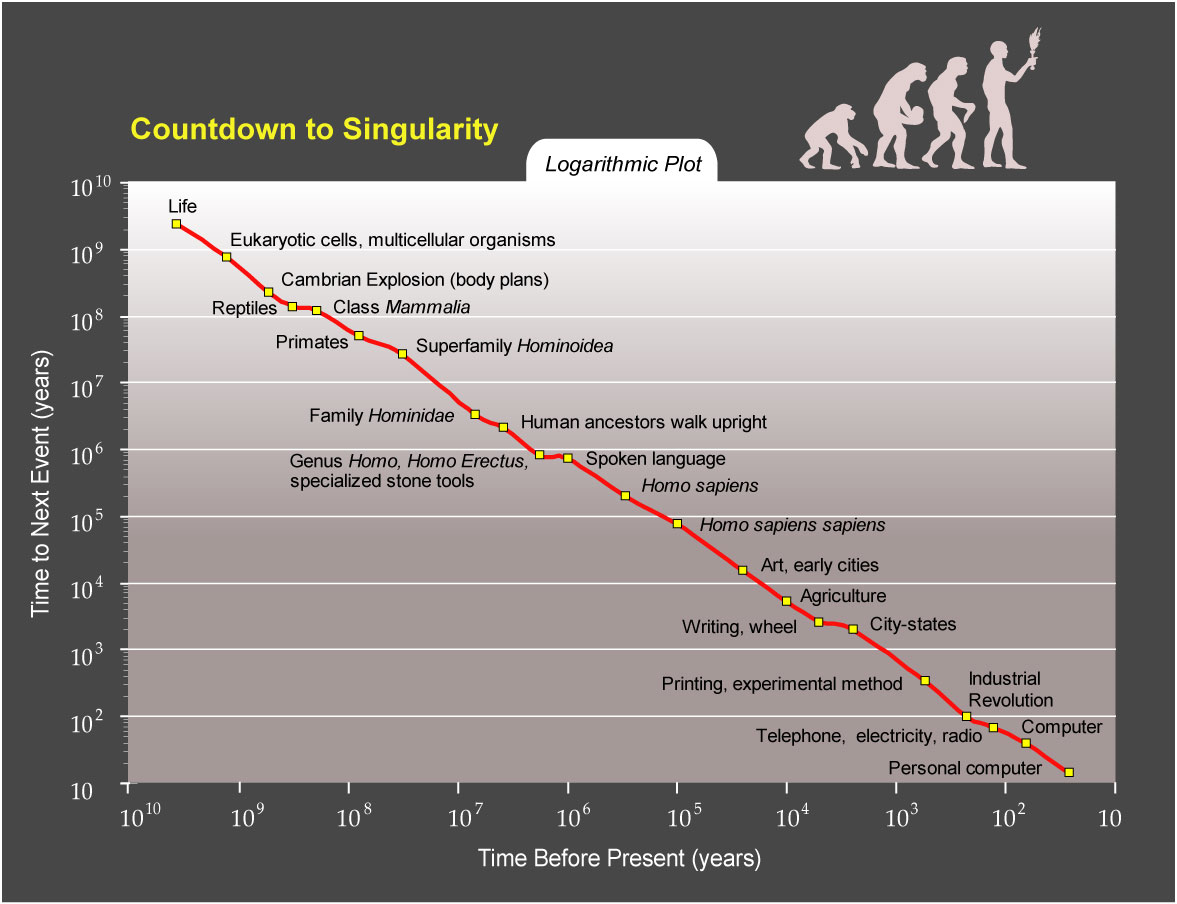
Artificial intelligence and the technological singularity
The concept of thetechnological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the m ...
, or the ultra-rapid advent of superhuman intelligence, was first proposed by the British cryptologist
This is a list of cryptographers. Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties called adversaries.
Pre twentieth century
* Al-Khalil ibn Ahmad al-Farahidi: wrote a (now lost) bo ...
I. J. Good in 1965:
Computer scientist Marvin Minsky
Marvin Lee Minsky (August 9, 1927 – January 24, 2016) was an American cognitive and computer scientist concerned largely with research of artificial intelligence (AI), co-founder of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's AI laboratory, ...
wrote on relationships between human and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
beginning in the 1960s. Over the succeeding decades, this field continued to generate influential thinkers such as Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings ...
and Raymond Kurzweil
Raymond Kurzweil ( ; born February 12, 1948) is an American computer scientist, author, inventor, and futurist. He is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), text-to-speech synthesis, speech recognition technology, and e ...
, who oscillated between the technical arena and futuristic speculations in the transhumanist vein. The coalescence of an identifiable transhumanist movement began in the last decades of the 20th century. In 1966, FM-2030 (formerly F. M. Esfandiary), a futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities abo ...
who taught "new concepts of the human" at The New School
The New School is a private research university in New York City. It was founded in 1919 as The New School for Social Research with an original mission dedicated to academic freedom and intellectual inquiry and a home for progressive thinkers. ...
, in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, began to identify people who adopt technologies, lifestyles and world views transitional to posthumanity as "transhuman
Transhuman, or trans-human, is the concept of an intermediary form between human and posthuman. In other words, a transhuman is a being that resembles a human in most respects but who has powers and abilities beyond those of standard humans. Th ...
". In 1972, Robert Ettinger
Robert Chester Wilson Ettinger (December 4, 1918 – July 23, 2011) was an American academic, known as "the father of cryonics" because of the impact of his 1962 book ''The Prospect of Immortality''.
Ettinger founded the Cryonics Institute ...
, whose 1964 ''Prospect of Immortality'' founded the cryonics movement, contributed to the conceptualization of "transhumanity" with his 1972 ''Man into Superman.'' FM-2030 published the ''Upwingers Manifesto'' in 1973.
Growth of transhumanism
The first self-described transhumanists met formally in the early 1980s at theUniversity of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California S ...
, which became the main center of transhumanist thought. Here, FM-2030 lectured on his "Third Way
The Third Way is a centrist political position that attempts to reconcile right-wing and left-wing politics by advocating a varying synthesis of centre-right economic policies with centre-left social policies. The Third Way was born from ...
" futurist ideology. At the EZTV
EZTV was a TV torrent distribution group founded in May 2005 and dissolved in April 2015, after a hostile takeover of their domains and brand by "EZCLOUD LIMITED". It quickly became the most visited torrent site for TV shows.
History
Founding ...
Media venue, frequented by transhumanists and other futurists, Natasha Vita-More
Natasha Vita-More (born February 23, 1950) is a strategic designer, author, speaker and innovator within the scientific and technological framework of human enhancement and life extension. Her interests are located within the ethical uses of scie ...
presented ''Breaking Away'', her 1980 experimental film with the theme of humans breaking away from their biological limitations and the Earth's gravity as they head into space. FM-2030 and Vita-More soon began holding gatherings for transhumanists in Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
, which included students from FM-2030's courses and audiences from Vita-More's artistic productions. In 1982, Vita-More authored the ''Transhumanist Arts Statement'' and, six years later, produced the cable TV show ''TransCentury Update ''on transhumanity, a program which reached over 100,000 viewers.
In 1986, Eric Drexler
Kim Eric Drexler (born April 25, 1955) is an American engineer best known for studies of the potential of molecular nanotechnology (MNT), from the 1970s and 1980s. His 1991 doctoral thesis at Massachusetts Institute of Technology was revised and ...
published '' Engines of Creation: The Coming Era of Nanotechnology,'' which discussed the prospects for nanotechnology and molecular assembler
A molecular assembler, as defined by K. Eric Drexler, is a "proposed device able to guide chemical reactions by positioning reactive molecules with atomic precision". A molecular assembler is a kind of molecular machine. Some biological molecul ...
s, and founded the Foresight Institute
The Foresight Institute (Foresight) is a San Francisco-based research non-profit that promotes the development of nanotechnology and other emerging technologies, such as safe AGI, biotech and longevity.
Foresight runs four cross-disciplinary pr ...
. As the first non-profit organization to research, advocate for, and perform cryonics
Cryonics (from el, κρύος ''kryos'' meaning 'cold') is the low-temperature freezing (usually at ) and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future. Cryonics is regarded with skepticis ...
, the Southern California offices of the Alcor Life Extension Foundation
The Alcor Life Extension Foundation, most often referred to as Alcor, is an American nonprofit, federally tax-exempt, 501(c)(3) organization based in Scottsdale, Arizona, United States. Alcor advocates for, researches, and performs cryonics, th ...
became a center for futurists. In 1988, the first issue of ''Extropy Magazine'' was published by Max More and Tom Morrow. In 1990, More, a strategic philosopher, created his own particular transhumanist doctrine, which took the form of the ''Principles of Extropy,'' and laid the foundation of modern transhumanism by giving it a new definition:
In 1992, More and Morrow founded the Extropy Institute
Extropianism, also referred to as the philosophy of extropy, is an "evolving framework of values and standards for continuously improving the human condition".
Extropians believe that advances in science and technology will some day let people l ...
, a catalyst for networking futurists and brainstorming new memeplex
Much of the study of memes focuses on groups of memes called meme complexes, or memeplexes. Like the gene complexes found in biology, memeplexes are groups of memes that are often found present in the same individual. Applying the theory of U ...
es by organizing a series of conferences and, more importantly, providing a mailing list, which exposed many to transhumanist views for the first time during the rise of cyberculture
Internet culture is a culture based on the many way people have used computer networks and their use for communication, entertainment, business, and recreation. Some features of Internet culture include online communities, gaming, and social medi ...
and the cyberdelic
Cyberdelic (from " cyber-" and "psychedelic") was the fusion of cyberculture and the psychedelic subculture that formed a new counterculture in the 1980s and 1990s.
Cyberdelic art was created by calculating fractal objects and representing the ...
counterculture. In 1998, philosophers Nick Bostrom and David Pearce founded the World Transhumanist Association
Humanity+ (also Humanity Plus; formerly the World Transhumanist Association) is a non-profit international educational organization that advocates the ethical use of technologies and evidence-based science to improve the human condition. This cond ...
(WTA), an international non-governmental organization working toward the recognition of transhumanism as a legitimate subject of scientific inquiry
Models of scientific inquiry have two functions: first, to provide a descriptive account of ''how'' scientific inquiry is carried out in practice, and second, to provide an explanatory account of ''why'' scientific inquiry succeeds as well as it ap ...
and public policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to solve or address relevant and real-world problems, guided by a conception and often implemented by programs. Public p ...
. In 2002, the WTA modified and adopted ''The Transhumanist Declaration.'' ''The Transhumanist FAQ'', prepared by the WTA (later Humanity+
Humanity most commonly refers to:
* Humankind, the total population of humans
* Humanity (virtue)
Humanity may also refer to:
Literature
* ''Humanity'' (journal), an academic journal that focuses on human rights
* ''Humanity: A Moral History of ...
), gave two formal definitions for transhumanism:
In possible contrast with other transhumanist organizations, WTA officials considered that social forces could undermine their futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities abo ...
visions and needed to be addressed. A particular concern is the equal access to human enhancement
Human enhancement (HE) can be described as the natural, artificial, or technological alteration of the human body in order to enhance physical or mental capabilities.
Technologies
Existing technologies
Three forms of human enhancement curre ...
technologies across classes and borders. In 2006, a political struggle within the transhumanist movement between the libertarian right and the liberal left
The Liberal Left (''Sinistra Liberale'', SL) was a minor liberal faction within the Democrats of the Left, an Italian political party.
It was formed basically by former left-wingers of the Italian Liberal Party. Its leaders include Gianfranco P ...
resulted in a more centre-left
Centre-left politics lean to the left on the left–right political spectrum but are closer to the centre than other left-wing politics. Those on the centre-left believe in working within the established systems to improve social justice. The ...
ward positioning of the WTA under its former executive director James Hughes. In 2006, the board of directors of the Extropy Institute ceased operations of the organization, stating that its mission was "essentially completed". This left the World Transhumanist Association as the leading international transhumanist organization. In 2008, as part of a rebranding effort, the WTA changed its name to "Humanity+
Humanity most commonly refers to:
* Humankind, the total population of humans
* Humanity (virtue)
Humanity may also refer to:
Literature
* ''Humanity'' (journal), an academic journal that focuses on human rights
* ''Humanity: A Moral History of ...
". In 2012, the transhumanist Longevity Party had been initiated as an international union of people who promote the development of scientific and technological means to significant life extension, that for now has more than 30 national organisations throughout the world.
The Mormon Transhumanist Association was founded in 2006. By 2012, it consisted of hundreds of members.
The first transhumanist elected member of a parliament has been Giuseppe Vatinno, in Italy.
Theory
It is a matter of debate whether transhumanism is a branch ofposthumanism
Posthumanism or post-humanism (meaning "after humanism" or "beyond humanism") is an idea in continental philosophy and critical theory responding to the presence of anthropocentrism in 21st century thought. It encompasses a wide variety of b ...
and how this philosophical movement should be conceptualised with regard to transhumanism. The latter is often referred to as a variant or activist form of posthumanism by its conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
, Christian and progressive critics.
A common feature of transhumanism and philosophical posthumanism is the future vision of a new intelligent species, into which humanity will evolve and eventually will supplement or supersede it. Transhumanism stresses the evolutionary perspective, including sometimes the creation of a highly intelligent animal species by way of cognitive enhancement (i.e. biological uplift
In science fiction, uplift is a developmental process to transform a certain species of animals into more intelligent beings by other, already-intelligent beings. This is usually accomplished by cultural, technological, or evolutional intervention ...
), but clings to a "posthuman future" as the final goal of participant evolution.
Nevertheless, the idea of creating intelligent artificial beings (proposed, for example, by roboticist Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings ...
) has influenced transhumanism. Moravec's ideas and transhumanism have also been characterised as a "complacent" or " apocalyptic" variant of posthumanism and contrasted with " cultural posthumanism" in humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at the t ...
and the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
. While such a "cultural posthumanism" would offer resources for rethinking the relationships between humans and increasingly sophisticated machines, transhumanism and similar posthumanisms are, in this view, not abandoning obsolete concepts of the " autonomous liberal subject", but are expanding its "prerogative
In law, a prerogative is an exclusive right bestowed by a government or state and invested in an individual or group, the content of which is separate from the body of rights enjoyed under the general law. It was a common facet of feudal law. The ...
s" into the realm of the posthuman. Transhumanist self-characterisations as a continuation of humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and Agency (philosophy), agency of Human, human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical in ...
and Enlightenment thinking correspond with this view.
Some secular humanists
Secular humanism is a philosophy, belief system or life stance that embraces human reason, secular ethics, and philosophical naturalism while specifically rejecting religious dogma, supernaturalism, and superstition as the basis of morality an ...
conceive transhumanism as an offspring of the humanist freethought movement and argue that transhumanists differ from the humanist mainstream by having a specific focus on technological approaches to resolving human concerns (i.e. technocentrism
Technocentrism is a value system that is centered on technology and its ability to control and protect the environment. Technocentrics argue that technology can address ecological problems through its problem-solving ability, efficiency, and its m ...
) and on the issue of mortality. However, other progressives have argued that posthumanism, whether it be its philosophical or activist forms, amounts to a shift away from concerns about social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, Equal opportunity, opportunities, and Social privilege, privileges within a society. In Western Civilization, Western and Culture of Asia, Asian cultures, the concept of social ...
, from the reform of human institutions and from other Enlightenment preoccupations, toward narcissistic
Narcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance or image and an excessive preoccupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
Narcissism exists on a co ...
longings for a transcendence of the human body in quest of more exquisite ways of being.
As an alternative, humanist philosopher Dwight Gilbert Jones has proposed a renewed Renaissance humanism through DNA and genome repositories, with each individual genotype ( DNA) being instantiated as successive phenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or phenotypic trait, traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (biology), morphology or physical form and structure, its Developmental biology, dev ...
(bodies or lives via cloning, ''Church of Man'', 1978). In his view, native molecular DNA "continuity" is required for retaining the "self" and no amount of computing power or memory aggregation can replace the essential "stink" of our true genetic identity, which he terms "genity". Instead, DNA/genome stewardship by an institution analogous to the Jesuits' 400 year vigil is a suggested model for enabling humanism to become our species' common credo, a project he proposed in his speculative novel ''The Humanist – 1000 Summers'' (2011), wherein humanity dedicates these coming centuries to harmonizing our planet and peoples.
The philosophy of transhumanism is closely related to technoself studies, an interdisciplinary domain of scholarly research dealing with all aspects of human identity in a technological society and focusing on the changing nature of relationships between humans and technology.
Aims
 While many transhumanist theorists and advocates seek to apply
While many transhumanist theorists and advocates seek to apply reason
Reason is the capacity of consciously applying logic by drawing conclusions from new or existing information, with the aim of seeking the truth. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, ...
, science and technology for the purposes of reducing poverty, disease, disability and malnutrition around the globe, transhumanism is distinctive in its particular focus on the applications of technologies to the improvement of human bodies at the individual level. Many transhumanists actively assess the potential for future technologies and innovative social systems to improve the quality of all life, while seeking to make the material reality of the human condition fulfill the promise of legal and political equality by eliminating congenital mental and physical barriers.
Transhumanist philosophers argue that there not only exists a perfectionist ethical imperative for humans to strive for progress and improvement of the human condition, but that it is possible and desirable for humanity to enter a transhuman
Transhuman, or trans-human, is the concept of an intermediary form between human and posthuman. In other words, a transhuman is a being that resembles a human in most respects but who has powers and abilities beyond those of standard humans. Th ...
phase of existence in which humans enhance themselves beyond what is naturally human. In such a phase, natural evolution would be replaced with deliberate participatory or directed evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis ( ...
.
Some theorists such as Ray Kurzweil
Raymond Kurzweil ( ; born February 12, 1948) is an American computer scientist, author, inventor, and futurist. He is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), text-to-speech synthesis, speech recognition technology, and e ...
think that the pace of technological innovation is accelerating and that the next 50 years may yield not only radical technological advances, but possibly a technological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the m ...
, which may fundamentally change the nature of human beings. Transhumanists who foresee this massive technological change generally maintain that it is desirable. However, some are also concerned with the possible dangers of extremely rapid technological change and propose options for ensuring that advanced technology is used responsibly. For example, Bostrom has written extensively on existential risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
s to humanity's future welfare, including ones that could be created by emerging technologies. In contrast, some proponents of transhumanism view it as essential to humanity's survival. For instance, Stephen Hawking points out that the "external transmission" phase of human evolution, where knowledge production
Knowledge can be defined as awareness of facts or as practical skills, and may also refer to familiarity with objects or situations. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often defined as true belief that is distinc ...
and knowledge management
Knowledge management (KM) is the collection of methods relating to creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. It refers to a multidisciplinary approach to achieve organisational objectives by making ...
is more important than transmission of information via evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, may be the point at which human civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Civi ...
becomes unstable and self-destructs, one of Hawking's explanations for the Fermi paradox
The Fermi paradox is the discrepancy between the lack of conclusive evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life and the apparently high a priori likelihood of its existence, and by extension of obtaining such evidence. As a 2015 article put it, ...
. To counter this, Hawking emphasizes either self-design of the human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the ...
or mechanical enhancement (e.g., brain-computer interface) to enhance human intelligence
Human intelligence is the intellectual capability of humans, which is marked by complex cognitive feats and high levels of motivation and self-awareness. High intelligence is associated with better outcomes in life.
Through intelligence, humans ...
and reduce aggression, without which he implies human civilization may be too stupid collectively to survive an increasingly unstable system, resulting in societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of socioeconomic complexity, the downfall of government, and the rise of violence. Possible cause ...
.
While many people believe that all transhumanists are striving for immortality, it is not necessarily true. Hank Pellissier, managing director of the Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies (2011–2012), surveyed transhumanists. He found that, of the 818 respondents, 23.8% did not want immortality.Pellissier, Hank. "Do all Transhumanists Want Immortality? No? Why Not?" Futurist 46.6 (2012): 65-. Web. Some of the reasons argued were boredom, Earth's overpopulation and the desire "to go to an afterlife".
Empathic fallibility and conversational consent
Certain transhumanist philosophers hold that since all assumptions about what others experience are fallible, and that therefore all attempts to help or protect beings that are not capable of correcting what others assume about them no matter how well-intentioned are in danger of actually hurting them, allsentient
Sentience is the capacity to experience feelings and sensations. The word was first coined by philosophers in the 1630s for the concept of an ability to feel, derived from Latin '' sentientem'' (a feeling), to distinguish it from the ability to ...
beings deserve to be sapient. These thinkers argue that the ability to discuss in a falsification-based way constitutes a threshold that is not arbitrary at which it becomes possible for an individual to speak for themselves in a way that is not dependent on exterior assumptions. They also argue that all beings capable of experiencing something deserve to be elevated to this threshold if they are not at it, typically stating that the underlying change that leads to the threshold is an increase in the preciseness of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
's ability to discriminate. This includes increasing the neuron count and connectivity in animals as well as accelerating the development of connectivity to shorten or ideally skip non-sapient childhood incapable of independently deciding for oneself. Transhumanists of this description stress that the genetic engineering that they advocate is general insertion into both the somatic cells of living beings and in germ cells, and not purging of individuals without the modifications, deeming the latter not only unethical but also unnecessary due to the possibilities of efficient genetic engineering.
Ethics
Transhumanists engage in interdisciplinary approaches to understand and evaluate possibilities for overcoming biological limitations by drawing onfuturology
Futures studies, futures research, futurism or futurology is the systematic, interdisciplinary and holistic study of social and technological advancement, and other environmental trends, often for the purpose of exploring how people will li ...
and various fields of ethics. Unlike many philosophers, social critics and activists who place a moral value on preservation of natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
systems, transhumanists see the very concept of the specifically natural
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
as problematically nebulous at best and an obstacle to progress at worst. In keeping with this, many prominent transhumanist advocates, such as Dan Agin, refer to transhumanism's critics, on the political right and left jointly, as " bioconservatives" or " bioluddites", the latter term alluding to the 19th century anti-industrialisation social movement that opposed the replacement of human manual labourers by machines.
A belief of counter-transhumanism is that transhumanism can cause unfair human enhancement in many areas of life, but specifically on the social plane. This can be compared to steroid use, where athletes who use steroids in sports have an advantage over those who do not. The same scenario happens when people have certain neural implants that give them an advantage in the work place and in educational aspects. Additionally, there are many, according to M.J. McNamee and S.D. Edwards, who fear that the improvements afforded by a specific, privileged section of society will lead to a division of the human species into two different and distinct species. The idea of two human species, one being at a great physical and economic advantage in comparison with the other, is a troublesome one at best. One may be incapable of breeding with the other, and may by consequence of lower physical health and ability, be considered of a lower moral standing than the other.
Nick Bostrom stated that transhumanism advocates for the wellbeing of all sentient beings, whether in non-human animals, extra-terrestrials or artificial forms of life. This view is reiterated by David Pearce, who advocates for the use of biotechnology to eradicate suffering in all sentient beings.
Currents
There is a variety of opinions within transhumanist thought. Many of the leading transhumanist thinkers hold views that are under constant revision and development. Some distinctive currents of transhumanism are identified and listed here in alphabetical order: * Abolitionism, the concept of using biotechnology to eradicate suffering in all sentient beings. * Democratic transhumanism, a political ideology synthesizingliberal democracy
Liberal democracy is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterized by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into ...
, social democracy
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote s ...
, radical democracy
Radical democracy is a type of democracy that advocates the radical extension of equality and liberty. Radical democracy is concerned with a radical extension of equality and freedom, following the idea that democracy is an unfinished, inclusive, ...
and transhumanism.
* Equalism, a socioeconomic theory based upon the idea that emerging technologies will put an end to social stratification through even distribution of resources in the technological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the m ...
era.
* Extropianism
Extropianism, also referred to as the philosophy of extropy, is an "evolving framework of values and standards for continuously improving the human condition".
Extropians believe that advances in science and technology will some day let people l ...
, an early school of transhumanist thought characterized by a set of principles advocating a proactive approach to human evolution.
* Immortalism, a moral ideology based upon the belief that radical life extension and technological immortality is possible and desirable, and advocating research and development to ensure its realization.
* Libertarian transhumanism
Transhumanist politics constitutes a group of political ideologies that generally express the belief in improving human individuals through science and technology.
History
The term "transhumanism" with its present meaning was popularised by J ...
, a political ideology synthesizing libertarianism and transhumanism.
* Postgenderism
Postgenderism is a social, political and cultural movement which arose from the eroding of the cultural, psychological, and social role of gender, and an argument for why the erosion of binary gender will be liberatory.
Postgenderists argue ...
, a social philosophy which seeks the voluntary elimination of gender
Gender is the range of characteristics pertaining to femininity and masculinity and differentiating between them. Depending on the context, this may include sex-based social structures (i.e. gender roles) and gender identity. Most cultures ...
in the human species through the application of advanced biotechnology and assisted reproductive technologies
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes ...
.
* Postpoliticism, a transhumanist political proposal that aims to create a " postdemocratic state" based on reason and free access of enhancement technologies to people.
*Singularitarianism
Singularitarianism is a movement defined by the belief that a technological singularity—the creation of superintelligence—will likely happen in the medium future, and that deliberate action ought to be taken to ensure that the singularity ben ...
, a moral ideology based upon the belief that a technological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable changes to human civilization. According to the m ...
is possible, and advocating deliberate action to effect it and ensure its safety.
* Technogaianism, an ecological ideology based upon the belief that emerging technologies can help restore Earth's environment and that developing safe, clean, alternative technology
Alternative technology is a term used to refer to technologies that are more environmentally friendly than the functionally equivalent technologies dominant in current practice. The term was coined by Peter Harper, one of the founders of the Centr ...
should therefore be an important goal of environmentalist
An environmentalist is a person who is concerned with and/or advocates for the protection of the environment. An environmentalist can be considered a supporter of the goals of the environmental movement, "a political and ethical movement that se ...
s.
Spirituality
Although many transhumanists areatheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
, agnostics
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
, and/or secular humanists
Secular humanism is a philosophy, belief system or life stance that embraces human reason, secular ethics, and philosophical naturalism while specifically rejecting religious dogma, supernaturalism, and superstition as the basis of morality an ...
, some have religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
or spiritual views. Despite the prevailing secular attitude, some transhumanists pursue hopes traditionally espoused by religions, such as immortality
Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some modern species may possess biological immortality.
Some scientists, futurists, and philosophers have theorized about the immortality of the human body, with some suggesting that human immorta ...
, while several controversial new religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or th ...
s from the late 20th century have explicitly embraced transhumanist goals of transforming the human condition by applying technology to the alteration of the mind and body, such as Raëlism
Raëlism, also known as Raëlianism or Raelian Movement is a UFO religion founded in 1970s France by Claude Vorilhon, now known as Raël. Scholars of religion classify Raëlism as a new religious movement. The group is formalised as the Inte ...
. However, most thinkers associated with the transhumanist movement focus on the practical goals of using technology to help achieve longer and healthier lives, while speculating that future understanding of neurotheology and the application of neurotechnology will enable humans to gain greater control of altered states of consciousness, which were commonly interpreted as spiritual experiences, and thus achieve more profound Self-knowledge (psychology), self-knowledge. Transhumanist Buddhists have sought to explore areas of agreement between various types of Buddhism and Buddhist meditation, Buddhist-derived meditation and mind-expanding neurotechnologies. However, they have been criticised for appropriating mindfulness as a tool for transcending humanness.
Some transhumanists believe in the compatibility between the human mind and computer hardware, with the theoretical implication that human consciousness may someday be transferred to alternative media (a speculative technique commonly known as mind uploading). One extreme formulation of this idea, which some transhumanists are interested in, is the proposal of the Omega Point by Christian cosmologist Frank J. Tipler, Frank Tipler. Drawing upon ideas in Digital physics, digitalism, Tipler has advanced the notion that the collapse of the Universe billions of years hence could create the conditions for the perpetuation of humanity in a simulated reality within a megacomputer and thus achieve a form of "posthuman God, posthuman godhood". Before Tipler, the term Omega Point was used by Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, a paleontologist and Jesuit theologian who saw an evolutionary telos (philosophy), telos in the development of an encompassing noosphere, a global consciousness.
Viewed from the perspective of some Christian thinkers, the idea of mind uploading is asserted to represent a #Contempt for the flesh, denigration of the human body, characteristic of gnostic manichaean belief. Transhumanism and its presumed intellectual progenitors have also been described as Gnosticism in modern times, neo-gnostic by non-Christian and secular commentators.
The first dialogue between transhumanism and faith was a one-day conference held at the University of Toronto in 2004. Religious critics alone faulted the philosophy of transhumanism as offering no eternal truths nor a relationship with the divinity, divine. They commented that a philosophy bereft of these beliefs leaves humanity adrift in a foggy sea of postmodern Cynicism (contemporary), cynicism and anomie. Transhumanists responded that such criticisms reflect a failure to look at the actual content of the transhumanist philosophy, which, far from being cynical, is rooted in optimistic, idealistic attitudes that trace back to the Enlightenment. Following this dialogue, William Sims Bainbridge, a sociology of religion, sociologist of religion, conducted a pilot study, published in the Journal of Evolution and Technology, suggesting that religious attitudes were negatively correlated with acceptance of transhumanist ideas and indicating that individuals with highly religious worldviews tended to perceive transhumanism as being a direct, competitive (though ultimately futile) affront to their spiritual beliefs.
Since 2006, the Mormon Transhumanist Association sponsors conferences and lectures on the intersection of technology and religion. The Christian Transhumanist Association was established in 2014.
Since 2009, the American Academy of Religion holds a "Transhumanism and Religion" consultation during its annual meeting, where scholars in the field of religious studies seek to identify and critically evaluate any implicit religious beliefs that might underlie key transhumanist claims and assumptions; consider how transhumanism challenges religious traditions to develop their own ideas of the human future, in particular the prospect of human transformation, whether by technological or other means; and provide critical and constructive assessments of an envisioned future that place greater confidence in nanotechnology, robotics and information technology to achieve virtual immortality and create a superior posthuman species.
The physicist and transhumanist thinker Giulio Prisco states that "cosmist religions based on science, might be our best protection from reckless pursuit of superintelligence and other risky technologies." Prisco also recognizes the importance of spiritual ideas, such as the ones of Russian Orthodox philosopher Nikolai Fyodorovich Fyodorov, to the origins of the transhumanism movement.
Practice
While some transhumanists take an abstract and theoretical approach to the perceived benefits of emerging technologies, others have offered specific proposals for modifications to the human body, including heritable ones. Transhumanists are often concerned with methods of enhancing the human nervous system. Though some, such as Kevin Warwick, propose modification of the peripheral nervous system, the human brain, brain is considered the common denominator of personhood and is thus a primary focus of transhumanist ambitions. In fact, Warwick has gone a lot further than merely making a proposal. In 2002 he had a 100 electrode array surgically implanted into the median nerves of his left arm to link his nervous system directly with a computer and thus to also connect with the internet. As a consequence, he carried out a series of experiments. He was able to directly control a robot hand using his neural signals and to feel the force applied by the hand through feedback from the fingertips. He also experienced a form of ultrasonic sensory input and conducted the first purely electronic communication between his own nervous system and that of his wife who also had electrodes implanted. As proponents of self-improvement and body modification, transhumanists tend to use existing technologies and techniques that supposedly improve cognitive and physical performance, while engaging in routines and lifestyles designed to improve health and longevity. Depending on their age, some transhumanists express concern that they will not live to reap the benefits of future technologies. However, many have a great interest in life extension strategies and in funding research in
As proponents of self-improvement and body modification, transhumanists tend to use existing technologies and techniques that supposedly improve cognitive and physical performance, while engaging in routines and lifestyles designed to improve health and longevity. Depending on their age, some transhumanists express concern that they will not live to reap the benefits of future technologies. However, many have a great interest in life extension strategies and in funding research in cryonics
Cryonics (from el, κρύος ''kryos'' meaning 'cold') is the low-temperature freezing (usually at ) and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future. Cryonics is regarded with skepticis ...
to make the latter a viable option of last resort, rather than remaining an unproven method. Regional and global transhumanist networks and communities with a range of objectives exist to provide support and forums for discussion and collaborative projects.
While most transhumanist theory focuses on future technologies and the changes they may bring, many today are already involved in the practice on a very basic level. It is not uncommon for many to receive cosmetic changes to their physical form via cosmetic surgery, even if it is not required for health reasons. Human growth hormones attempt to alter the natural development of shorter children or those who have been born with a physical deficiency. Doctors prescribe medicines such as Ritalin and Adderall to improve cognitive focus, and many people take "lifestyle" drugs such as Viagra, Propecia, and Botox to restore aspects of youthfulness that have been lost in maturity.
Other transhumanists, such as cyborg artist Neil Harbisson, use technologies and techniques to improve their senses and perception of reality. Harbisson's antenna, which is permanently implanted in his skull, allows him to sense colours beyond human perception such as infrareds and ultraviolets.
Technologies of interest
Transhumanists support the emerging technologies, emergence and converging technologies, convergence of technologies including nanotechnology, biotechnology, information technology and cognitive science (NBIC), as well as hypothetical future technologies like simulated reality,artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
, superintelligence, 3D bioprinting, mind uploading, chemical brain preservation and cryonics
Cryonics (from el, κρύος ''kryos'' meaning 'cold') is the low-temperature freezing (usually at ) and storage of human remains, with the speculative hope that resurrection may be possible in the future. Cryonics is regarded with skepticis ...
. They believe that humans can and should use these technologies to become superhuman, more than human. Therefore, they support the recognition and/or protection of cognitive liberty, morphological freedom and procreative liberty as civil liberties, so as to guarantee individuals the choice of using human enhancement technologies on themselves and their children. Some speculate that human enhancement techniques and other emerging technologies may facilitate more radical human enhancement no later than at the midpoint of the 21st century. Kurzweil's book ''The Singularity is Near'' and Michio Kaku's book ''Physics of the Future'' outline various human enhancement technologies and give insight on how these technologies may impact the human race.
Some reports on the converging technologies and NBIC concepts have criticised their transhumanist orientation and alleged science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel uni ...
al character. At the same time, research on brain and body alteration technologies has been accelerated under the sponsorship of the United States Department of Defense, U.S. Department of Defense, which is interested in the battlefield advantages they would provide to the supersoldiers of the United States and its allies. There has already been a brain research program to "extend the ability to manage information", while military scientists are now looking at stretching the human capacity for combat to a maximum 168 hours without sleep.
Neuroscientist Anders Sandberg has been practicing on the method of scanning ultra-thin sections of the brain. This method is being used to help better understand the architecture of the brain. As of now, this method is currently being used on mice. This is the first step towards hypothetically uploading contents of the human brain, including memories and emotions, onto a computer.
Debate
The very notion and prospect of human enhancement and related issues arouse public controversy. Criticisms of transhumanism and its proposals take two main forms: those objecting to the likelihood of transhumanist goals being achieved (practical criticisms) and those objecting to the moral principles or worldview sustaining transhumanist proposals or underlying transhumanism itself (ethical criticisms). Critics and opponents often see transhumanists' goals as posing threats to humanism, human values. Some of the most widely known critiques of the transhumanist program are novels and fictional films. These works of art, despite presenting imagined worlds rather than philosophical analyses, are used as touchstones for some of the more formal arguments. Various arguments have been made to the effect that a society that adopts human enhancement technologies may come to resemble the dystopia depicted in the 1932 novel ''Brave New World ''by Aldous Huxley. On another front, some authors consider that humanity is already transhuman, because medical advances in recent centuries have significantly altered our species. However, it is not in a conscious and therefore transhumanistic way. From such perspective, transhumanism is perpetually aspirational: as new technologies become mainstream, the adoption of new yet-unadopted technologies becomes a new shifting goal.Feasibility
In a 1992 book, sociologist Max Dublin pointed to many past failed predictions of technological progress and argued that modern futurist predictions would prove similarly inaccurate. He also objected to what he saw as scientism, fanaticism and nihilism by a few in advancing transhumanist causes. Dublin also said that historical parallels existed between Millenarianism, Millenarian religions and Historical materialism, Communist doctrines. Although generally sympathetic to transhumanism, public health professor Gregory Stock is skeptical of the technical feasibility and mass appeal of the cyborgization of humanity predicted by Raymond Kurzweil,Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings ...
and Kevin Warwick. He said that, throughout the 21st century, many humans would find themselves deeply integrated into systems of machines, but would remain biological. Primary changes to their own form and character would arise not from cyberware, but from the direct manipulation of their genetics, metabolism and biochemistry.
In her 1992 book ''Science as Salvation'', philosopher Mary Midgley traces the notion of achieving immortality by transcendence of the material human body (echoed in the transhumanist tenet of mind uploading) to a group of male scientific thinkers of the early 20th century, including J. B. S. Haldane
John Burdon Sanderson Haldane (; 5 November 18921 December 1964), nicknamed "Jack" or "JBS", was a British-Indian scientist who worked in physiology, genetics, evolutionary biology, and mathematics. With innovative use of statistics in biolog ...
and members of his circle. She characterizes these ideas as "quasi-scientific dreams and prophesies" involving Escapism, visions of escape from the body coupled with "self-indulgent, uncontrolled power-fantasies". Her argument focuses on what she perceives as the pseudoscientific speculations and irrational, fear-of-death-driven fantasies of these thinkers, their disregard for layman, laymen and the remoteness of their eschatological visions.
Another critique is aimed mainly at "algeny" (a portmanteau of ''alchemy'' and ''genetics''), which Jeremy Rifkin defined as "the upgrading of existing organisms and the design of wholly new ones with the intent of 'perfecting' their performance". It emphasizes the issue of biocomplexity and the unpredictability of attempts to guide the development of products of biological evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
. This argument, elaborated in particular by the biologist Stuart Newman, is based on the recognition that somatic cell nuclear transfer, cloning and germline genetic engineering of animals are error-prone and inherently disruptive of embryonic morphogenesis, development. Accordingly, so it is argued, it would create unacceptable risks to use such methods on human embryos. Performing experiments, particularly ones with permanent biological consequences, on developing humans would thus be in violation of accepted principles governing research on human subjects (see the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki). Moreover, because improvements in experimental outcomes in one species are not automatically transferable to a new species without further experimentation, it is claimed that there is no ethical route to genetic manipulation of humans at early developmental stages.
As a practical matter, however, international protocols on human subject research may not present a legal obstacle to attempts by transhumanists and others to improve their offspring by germinal choice technology. According to legal scholar Kirsten Rabe Smolensky, existing laws would protect parents who choose to enhance their child's genome from future liability arising from adverse outcomes of the procedure.
Transhumanists and other supporters of human genetic engineering do not dismiss practical concerns out of hand, insofar as there is a high degree of uncertainty about the timelines and likely outcomes of genetic modification experiments in humans. However, bioethicist James Hughes suggests that one possible ethical route to the genetic manipulation of humans at early developmental stages is the building of computer models of the human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the ...
, the proteins it specifies and the tissue engineering he argues that it also codes for. With the exponential progress in bioinformatics, Hughes believes that a virtual model of genetic expression in the human body will not be far behind and that it will soon be possible to accelerate approval of genetic modifications by simulating their effects on virtual humans. Public health professor Gregory Stock points to Human artificial chromosome, artificial chromosomes as an alleged safer alternative to existing genetic engineering techniques.
Thinkers who defend the likelihood of accelerating change point to a past pattern of exponential increases in humanity's technological capacities. Kurzweil developed this position in his 2005 book ''The Singularity Is Near''.
Intrinsic immorality
It has been argued that, in transhumanist thought, humans attempt to substitute themselves for God. The 2002 Holy See, Vatican statement ''Communion and Stewardship: Human Persons Created in the Image of God,'' stated that "changing the genetic identity of man as a human person through the production of an infrahuman being is radically immoral", implying, that "man has full right of disposal over his own biological nature". The statement also argues that creation of a superhuman or spiritually superior being is "unthinkable", since true improvement can come only through religious experience and "Divinization (Christian), realizing more fully the image of God". Christian theologians and lay activists of several churches and denominations have expressed similar objections to transhumanism and claimed that Christians attain in the afterlife what radical transhumanism promises, such as indefinite life extension or the abolition of suffering. In this view, transhumanism is just another representative of the long line of utopian movements which seek to immanentize the eschaton, create "heaven on earth". On the other hand, religious thinkers allied with transhumanist goals such as the theologians Ronald Cole-Turner and Ted Peters (theologian), Ted Peters hold that the doctrine of "co-creation" provides an obligation to use genetic engineering to improve human biology. Other critics target what they claim to be an instrumental conception of the human body in the writings of Marvin Minsky,Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings ...
and some other transhumanists. Reflecting a strain of feminism, feminist criticism of the transhumanist program, philosopher Susan Bordo points to "contemporary Body image, obsessions with slenderness, youth and physical perfection", which she sees as affecting both men and women, but in distinct ways, as "the logical (if extreme) manifestations of anxieties and fantasies fostered by our culture." Some critics question other social implications of the movement's focus on body modification. Political scientist Klaus-Gerd Giesen, in particular, has asserted that transhumanism's concentration on altering the human body represents the logical yet tragic consequence of atomized individualism and body commodification within a consumer culture.
Nick Bostrom responds that the desire to rejuvenation (aging), regain youth, specifically, and transcend the natural limitations of the human body, in general, is pan-cultural and pan-historical, and is therefore not uniquely tied to the culture of the 20th century. He argues that the transhumanist program is an attempt to channel that desire into a scientific project on par with the Human Genome Project and achieve humanity's oldest hope, rather than a puerile fantasy or social trend.
Loss of human identity
 In his 2003 book ''Enough: Staying Human in an Engineered Age'', environmental ethics, environmental ethicist Bill McKibben argued at length against many of the technologies that are postulated or supported by transhumanists, including germinal choice technology, nanomedicine and life extension strategies. He claims that it would be morally wrong for humans to tamper with fundamental aspects of themselves (or their children) in an attempt to overcome universal human limitations, such as vulnerability to aging, maximum life span and biological constraints on physical and cognitive ability. Attempts to "improve" themselves through such manipulation would remove limitations that provide a necessary context for the experience of meaningful human choice. He claims that human lives would no longer seem Meaning of life, meaningful in a world where such limitations could be overcome technologically. Even the goal of using germinal choice technology for clearly therapeutic purposes should be relinquished, since it would inevitably produce temptations to tamper with such things as cognitive capacities. He argues that it is possible for societies to benefit from renouncing particular technologies, using as examples Ming Dynasty, Ming China, Tokugawa shogunate, Tokugawa Japan and the contemporary Amish.
Biopolitical activist Jeremy Rifkin and biologist Stuart Newman accept that biotechnology has the power to make profound changes in organismal identity. They argue against the genetic engineering of human beings because they fear the blurring of the boundary between human and Cultural artifact, artifact. Philosopher Keekok Lee sees such developments as part of an accelerating trend in modernization in which technology has been used to transform the "natural" into the "artefactual". In the extreme, this could lead to the manufacturing and enslavement of "monsters" such as human clones, human-animal hybrid, human-animal chimera (genetics), chimeras, or bioroids, but even lesser dislocations of humans and non-humans from social structure, social and ecosystem, ecological systems are seen as problematic. The film ''Blade Runner'' (1982) and the novels ''The Boys from Brazil (novel), The Boys From Brazil'' (1976) and ''The Island of Doctor Moreau'' (1896) depict elements of such scenarios, but Mary Shelley's 1818 novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus '' is most often alluded to by critics who suggest that biotechnologies could create objectification, objectified and anomie, socially unmoored people as well as untermensch, subhumans. Such critics propose that strict measures be implemented to prevent what they portray as dehumanization, dehumanizing possibilities from ever happening, usually in the form of an international ban (law), ban on human genetic engineering.
Science journalist Ronald Bailey claims that McKibben's historical examples are flawed and support different conclusions when studied more closely. For example, few groups are more cautious than the Amish about embracing new technologies, but, though they shun television and use horses and buggies, some are welcoming the possibilities of gene therapy since inbreeding has afflicted them with a number of rare genetic diseases. Bailey and other supporters of technological alteration of human biology also reject the claim that life would be experienced as meaningless if some human limitations are overcome with enhancement technologies as extremely subjective.
Writing in ''Reason (magazine), Reason'' magazine, Bailey has accused opponents of research involving the modification of animals as indulging in alarmism when they speculate about the creation of subhuman creatures with human-like intelligence and brains resembling those of ''Homo sapiens''. Bailey insists that the aim of conducting research on animals is simply to produce human health care benefits.
A different response comes from transhumanist personhood theory, personhood theorists who object to what they characterize as the anthropomorphobia fueling some criticisms of this research, which science fiction writer Isaac Asimov termed the "Frankenstein complex". For example, Woody Evans argues that, provided they are self-aware, human clones, human-animal chimeras and biological uplift, uplifted animals would all be unique persons deserving of respect, dignity, rights, responsibilities, and citizenship. They conclude that the coming ethical issue is not the creation of so-called monsters, but what they characterize as the "wisdom of repugnance, yuck factor" and "Human exceptionalism, human-racism", that would judge and treat these creations as monstrous. In book 3 of his ''Corrupting the Image'' series, Dr. Douglas Hamp goes so far as to suggest that the Beast of John's Apocalypse is himself a hybrid who will induce humanity to take "the Number of the beast, mark of the Beast," in the hopes of obtaining perfection and immortality.
At least one public interest organization, the U.S.-based Center for Genetics and Society, was formed, in 2001, with the specific goal of opposing transhumanist agendas that involve transgenerational modification of human biology, such as full-term human cloning and germinal choice technology. The Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future of the Chicago-Kent College of Law critically scrutinizes proposed applications of genetic and nanotechnologies to human biology in an academic setting.
In his 2003 book ''Enough: Staying Human in an Engineered Age'', environmental ethics, environmental ethicist Bill McKibben argued at length against many of the technologies that are postulated or supported by transhumanists, including germinal choice technology, nanomedicine and life extension strategies. He claims that it would be morally wrong for humans to tamper with fundamental aspects of themselves (or their children) in an attempt to overcome universal human limitations, such as vulnerability to aging, maximum life span and biological constraints on physical and cognitive ability. Attempts to "improve" themselves through such manipulation would remove limitations that provide a necessary context for the experience of meaningful human choice. He claims that human lives would no longer seem Meaning of life, meaningful in a world where such limitations could be overcome technologically. Even the goal of using germinal choice technology for clearly therapeutic purposes should be relinquished, since it would inevitably produce temptations to tamper with such things as cognitive capacities. He argues that it is possible for societies to benefit from renouncing particular technologies, using as examples Ming Dynasty, Ming China, Tokugawa shogunate, Tokugawa Japan and the contemporary Amish.
Biopolitical activist Jeremy Rifkin and biologist Stuart Newman accept that biotechnology has the power to make profound changes in organismal identity. They argue against the genetic engineering of human beings because they fear the blurring of the boundary between human and Cultural artifact, artifact. Philosopher Keekok Lee sees such developments as part of an accelerating trend in modernization in which technology has been used to transform the "natural" into the "artefactual". In the extreme, this could lead to the manufacturing and enslavement of "monsters" such as human clones, human-animal hybrid, human-animal chimera (genetics), chimeras, or bioroids, but even lesser dislocations of humans and non-humans from social structure, social and ecosystem, ecological systems are seen as problematic. The film ''Blade Runner'' (1982) and the novels ''The Boys from Brazil (novel), The Boys From Brazil'' (1976) and ''The Island of Doctor Moreau'' (1896) depict elements of such scenarios, but Mary Shelley's 1818 novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus '' is most often alluded to by critics who suggest that biotechnologies could create objectification, objectified and anomie, socially unmoored people as well as untermensch, subhumans. Such critics propose that strict measures be implemented to prevent what they portray as dehumanization, dehumanizing possibilities from ever happening, usually in the form of an international ban (law), ban on human genetic engineering.
Science journalist Ronald Bailey claims that McKibben's historical examples are flawed and support different conclusions when studied more closely. For example, few groups are more cautious than the Amish about embracing new technologies, but, though they shun television and use horses and buggies, some are welcoming the possibilities of gene therapy since inbreeding has afflicted them with a number of rare genetic diseases. Bailey and other supporters of technological alteration of human biology also reject the claim that life would be experienced as meaningless if some human limitations are overcome with enhancement technologies as extremely subjective.
Writing in ''Reason (magazine), Reason'' magazine, Bailey has accused opponents of research involving the modification of animals as indulging in alarmism when they speculate about the creation of subhuman creatures with human-like intelligence and brains resembling those of ''Homo sapiens''. Bailey insists that the aim of conducting research on animals is simply to produce human health care benefits.
A different response comes from transhumanist personhood theory, personhood theorists who object to what they characterize as the anthropomorphobia fueling some criticisms of this research, which science fiction writer Isaac Asimov termed the "Frankenstein complex". For example, Woody Evans argues that, provided they are self-aware, human clones, human-animal chimeras and biological uplift, uplifted animals would all be unique persons deserving of respect, dignity, rights, responsibilities, and citizenship. They conclude that the coming ethical issue is not the creation of so-called monsters, but what they characterize as the "wisdom of repugnance, yuck factor" and "Human exceptionalism, human-racism", that would judge and treat these creations as monstrous. In book 3 of his ''Corrupting the Image'' series, Dr. Douglas Hamp goes so far as to suggest that the Beast of John's Apocalypse is himself a hybrid who will induce humanity to take "the Number of the beast, mark of the Beast," in the hopes of obtaining perfection and immortality.
At least one public interest organization, the U.S.-based Center for Genetics and Society, was formed, in 2001, with the specific goal of opposing transhumanist agendas that involve transgenerational modification of human biology, such as full-term human cloning and germinal choice technology. The Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future of the Chicago-Kent College of Law critically scrutinizes proposed applications of genetic and nanotechnologies to human biology in an academic setting.
Socioeconomic effects
Some critics of libertarian transhumanism have focused on the likely socioeconomic consequences in societies in which economic inequality, divisions between rich and poor are on the rise. Bill McKibben, for example, suggests that emerging human enhancement technologies would be disproportionately available to those with greater financial resources, thereby exacerbating the gap between rich and poor and creating a "genetic divide". Even Lee M. Silver, the biologist and science writer who coined the term "reprogenetics" and supports its applications, has expressed concern that these methods could create a two-tiered society of genetically engineered "haves" and "have nots" if social safety net, social democratic reforms lag behind implementation of enhancement technologies. The 1997 film ''Gattaca'' depicts a dystopian society in which one's social class depends entirely on genetic potential and is often cited by critics in support of these views. These criticisms are also voiced by criticism of libertarianism, non-libertarian transhumanist advocates, especially self-described democratic transhumanists, who believe that the majority of current or future social issues, social and environmental issues (such as unemployment and resource depletion) need to be addressed by a combination of political and technological solutions (like a guaranteed minimum income andalternative technology
Alternative technology is a term used to refer to technologies that are more environmentally friendly than the functionally equivalent technologies dominant in current practice. The term was coined by Peter Harper, one of the founders of the Centr ...
). Therefore, on the specific issue of an emerging genetic divide due to unequal access to human enhancement technologies, bioethicist James Hughes, in his 2004 book ''Citizen Cyborg, Citizen Cyborg: Why Democratic Societies Must Respond to the Redesigned Human of the Future'', argues that progressivism, progressives or, more precisely, techno-progressives must articulate and implement public policies (i.e., a universal health care voucher system that covers human enhancement technologies) to attenuate this problem as much as possible, rather than trying to ban human enhancement technologies. The latter, he argues, might actually worsen the problem by making these technologies unsafe or available only to the wealthy on the local black market or in countries where such a ban is not enforced.
Sometimes, as in the writings of Leon Kass, the fear is that various institutions and practices judged as fundamental to civilized society would be damaged or destroyed. In his 2002 book ''Our Posthuman Future'' and in a 2004 ''Foreign Policy (magazine), Foreign Policy'' magazine article, political economist and philosopher Francis Fukuyama designates transhumanism as the world's most dangerous idea because he believes that it may undermine the egalitarian ideals of democracy (in general) and liberal democracy
Liberal democracy is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterized by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into ...
(in particular) through a fundamental alteration of "human nature". Social philosopher Jürgen Habermas makes a similar argument in his 2003 book ''The Future of Human Nature'', in which he asserts that moral autonomy depends on not being subject to another's unilaterally imposed specifications. Habermas thus suggests that the human "species ethic" would be undermined by embryo-stage genetic alteration. Critics such as Kass, Fukuyama and a variety of authors hold that attempts to significantly alter human biology are not only inherently immoral, but also threaten the social order. Alternatively, they argue that implementation of such technologies would likely lead to the "naturalizing" of social hierarchy, social hierarchies or place new means of social control, control in the hands of totalitarianism, totalitarian regimes. AI pioneer Joseph Weizenbaum criticizes what he sees as misanthropic tendencies in the language and ideas of some of his colleagues, in particular Marvin Minsky and Hans Moravec
Hans Peter Moravec (born November 30, 1948, Kautzen, Austria) is an adjunct faculty member at the Robotics Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, USA. He is known for his work on robotics, artificial intelligence, and writings ...
, which, by devaluing the human organism per se, promotes a discourse that enables divisive and undemocratic social policies.
In a 2004 article in the libertarian monthly ''Reason (magazine), Reason,'' science journalist Ronald Bailey contested the assertions of Fukuyama by arguing that political equality has never rested on the facts of human biology. He asserts that liberalism was founded not on the proposition of effective equality of human beings, or ''de facto'' equality, but on the assertion of an equality in political rights and before the law, or ''de jure'' equality. Bailey asserts that the products of genetic engineering may well ameliorate rather than exacerbate human inequality, giving to the many what were once the privileges of the few. Moreover, he argues, "the crowning achievement of the Enlightenment is the principle of Toleration, tolerance". In fact, he says, political liberalism is already the solution to the issue of human and posthuman rights since in liberal societies the law is meant to apply equally to all, no matter how rich or poor, powerful or powerless, educated or ignorant, enhanced or unenhanced. Other thinkers who are sympathetic to transhumanist ideas, such as philosopher Russell Blackford, have also objected to the appeal to traditional values, tradition and what they see as alarmism involved in ''Brave New World''-type arguments.
Cultural aesthetics
In addition to the socio-economic risks and implications of transhumanism, there are indeed implications and possible consequences in regard to cultural aesthetics. Currently, there are a number of ways in which people choose to represent themselves in society. The way in which a person dresses, hair styles, and body alteration all serve to identify the way a person presents themselves and is perceived by society. According to Foucault, society already governs and controls bodies by making them feel watched. This "surveillance" of society dictates how the majority of individuals choose to express themselves aesthetically. One of the risks outlined in a 2004 article by Jerold Abrams is the elimination of differences in favor of universality. This, he argues, will eliminate the ability of individuals to subvert the possibly oppressive, dominant structure of society by way of uniquely expressing themselves externally. Such control over a population would have dangerous implications of tyranny. Yet another consequence of enhancing the human form not only cognitively, but physically, will be the reinforcement of "desirable" traits which are perpetuated by the dominant social structure. Physical traits which are seen as "ugly" or "undesirable" and thus deemed less-than, will be summarily cut out by those who can afford to do it, while those who cannot will be forced into a relative caste of undesirable people. Even if these physical "improvements" are made completely universal, they will indeed eliminate what makes each individual uniquely human in their own way.Specter of coercive eugenicism
Some critics of transhumanism see the oldeugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior o ...
, social Darwinist, and master race ideologies and programs of the past as warnings of what the promotion of eugenic enhancement technologies might unintentionally encourage. Some fear future "Biopolitics, eugenics wars" as the worst-case scenario: the return of coercive state-sponsored genetic discrimination and Human rights violations#Human rights violations, human rights violations such as compulsory sterilization of persons with genetic defects, the killing of the institutionalized and, specifically, racial segregation, segregation and genocide of Social interpretations of race, ''races'''' ''perceived as inferior. Health law professor George Annas and technology law professor Lori Andrews are prominent advocates of the position that the use of these technologies could lead to such human- posthuman caste warfare.
The major transhumanist organizations strongly condemn the coercion involved in such policies and reject the scientific racism, racist and classist assumptions on which they were based, along with the pseudoscientific notions that eugenic improvements could be accomplished in a practically meaningful time frame through selective human breeding. Instead, most transhumanist thinkers advocate a "new eugenics", a form of egalitarian liberal eugenics. In their 2000 book ''From Chance to Choice: Genetics and Justice'', non-transhumanist bioethicists Allen Buchanan, Dan Brock, Norman Daniels and Daniel Wikler have argued that liberal societies have an obligation to encourage as wide an adoption of eugenic enhancement technologies as possible (so long as such policies do not infringe on individuals' reproductive rights or exert undue pressures on prospective parents to use these technologies) to maximize public health and minimize the inequalities that may result from both natural genetic endowments and unequal access to genetic enhancements. Most transhumanists holding similar views nonetheless distance themselves from the term "eugenics" (preferring "germinal choice" or "reprogenetics") to avoid having their position confused with the discredited theories and practices of early-20th-century eugenic movements.
Existential risks
In his 2003 book ''Our Final Hour'', British Astronomer Royal Martin Rees argues that advanced science and technology bring as much risk of disaster as opportunity for progress. However, Rees does not advocate a halt to scientific activity. Instead, he calls for tighter security and perhaps an end to traditional scientific openness. Advocates of the precautionary principle, such as many in the environmental movement, also favor slow, careful progress or a halt in potentially dangerous areas. Some precautionists believe thatartificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
and robotics present possibilities of alternative forms of cognition that may threaten human life.
Transhumanists do not necessarily rule out specific restrictions on emerging technologies so as to lessen the prospect of existential risk
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical future event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanen ...
. Generally, however, they counter that proposals based on the precautionary principle are often technorealism, unrealistic and sometimes even counter-productive as opposed to the technogaian current of transhumanism, which they claim is both realistic and productive. In his television series ''Connections (British documentary), Connections'', science historian James Burke (science historian), James Burke dissects several views on technological change, including precautionism and the restriction of inquiry, open inquiry. Burke questions the practicality of some of these views, but concludes that maintaining the ''status quo'' of inquiry and development poses hazards of its own, such as a disorienting rate of change and the depletion of our planet's resources. The common transhumanist position is a pragmatic one where society takes deliberate action to ensure the early arrival of the benefits of safe, clean, alternative technology
Alternative technology is a term used to refer to technologies that are more environmentally friendly than the functionally equivalent technologies dominant in current practice. The term was coined by Peter Harper, one of the founders of the Centr ...
, rather than fostering what it considers to be anti-science, anti-scientific views and technophobia.
Nick Bostrom argues that even barring the occurrence of a singular Global catastrophic risk, global catastrophic event, basic Malthusian and evolutionary forces facilitated by technological progress threaten to eliminate the positive aspects of human society.
One transhumanist solution proposed by Bostrom to counter existential risks is control of differential technological development, a series of attempts to influence the sequence in which technologies are developed. In this approach, planners would strive to retard the development of possibly harmful technologies and their applications, while accelerating the development of likely beneficial technologies, especially those that offer protection against the harmful effects of others.
See also
References
Further reading
* Adorno, F.P. (2021) THe Transhumanist Movement, Palgrave MacMillan New York ISBN 978-3-030-82423-5 * * * * * Oliver Krüger: ''Virtual Immortality. God, Evolution, and the Singularity in Post- and Transhumanism.'', Bielefeld: transcript 2021. * * * * *External links
*H+Pedia
Transhumanist Wiki
What is Transhumanism?
*Future of Humanity Institute *Institute on Biotechnology and the Human Future {{Authority control Transhumanism, 1990 introductions Bioethics Body modification Doomsday scenarios, * Emerging technologies Ethics of science and technology Existential risk from artificial general intelligence Ideologies Immortality Metaphysics Ontology Philosophical movements Philosophy of artificial intelligence Philosophy of culture Philosophy of science Philosophy of technology Philosophical anthropology Posthumanism Science fiction culture Science fiction themes Singularitarianism Singularity theory Social change Social philosophy Subcultures Technological change Technology development Technology forecasting Technology hazards Theory of mind Transhumanist politics Technological utopianism